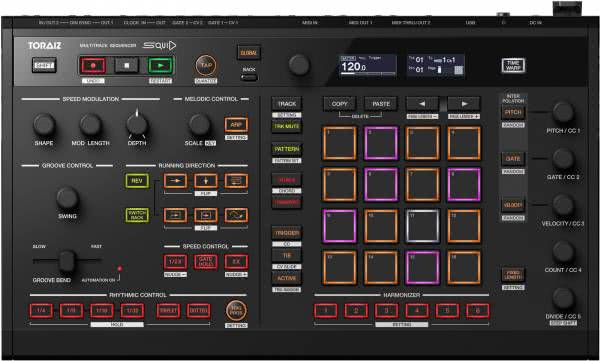
The right control element for each parameter
MIDI controllers have different controller elements. Not every element and ultimately not every MIDI controller is suitable for controlling individual parameters.
 Knobs are designed to control more constant parameters without the need for high precision. Ideal for effect parameters
Knobs are designed to control more constant parameters without the need for high precision. Ideal for effect parameters
Encoders are ideal for selecting files, for example for song or effect selection..
 Faders are suitable for parameters with high regulation precision such as volume or pitch shifters, and are mainly used with Daw controllers to make the software more precise.
Faders are suitable for parameters with high regulation precision such as volume or pitch shifters, and are mainly used with Daw controllers to make the software more precise.
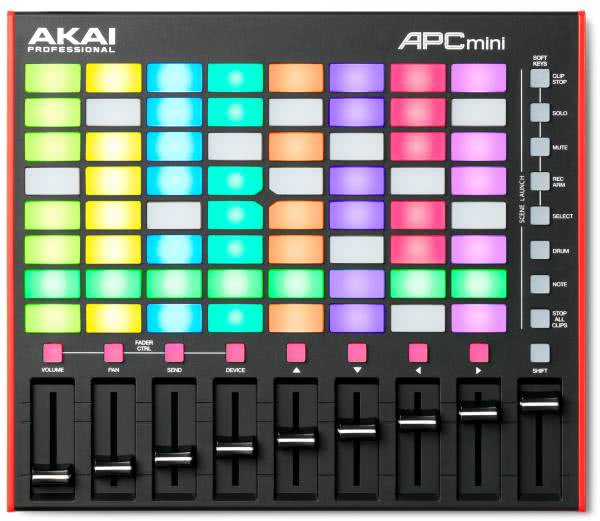
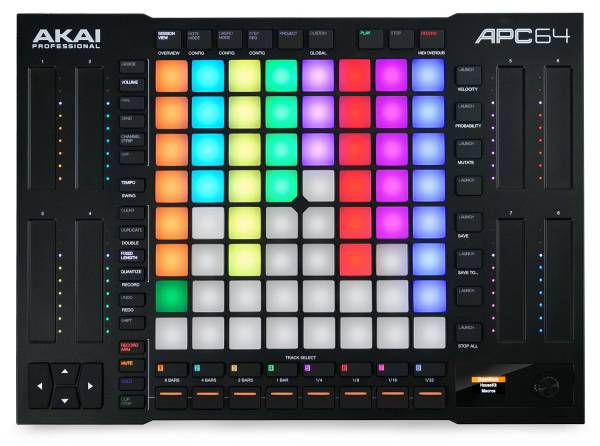
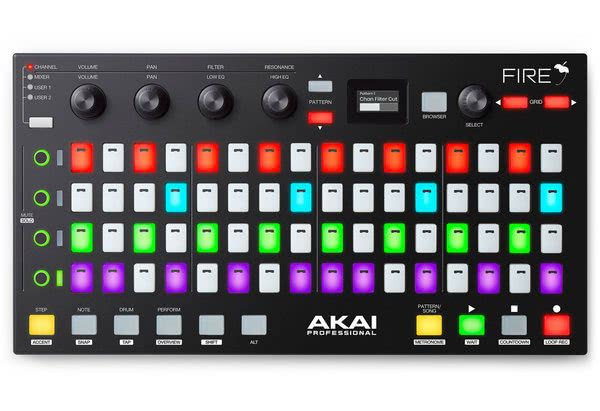
 Pads are suitable for all parameters with two states (on and off) without velocity, for example for on/off control of effects. Pads with velocity response are suitable for all parameters that require a velocity value in addition to on/off information.
Pads are suitable for all parameters with two states (on and off) without velocity, for example for on/off control of effects. Pads with velocity response are suitable for all parameters that require a velocity value in addition to on/off information.
Ideal for synthesizer sounds. Pad controllers are especially popular in hip-hop and electronic music.
Touchpads usually control three different parameters at the same time and are suitable for filter and synthesizer parameters.
Ribbon controllers are different from other MIDI controllers and contain a control box in addition to a control unit. The position and pressure sensor in the control box works without gradation. The information from the sensors only becomes control data and MIDI commands within the control box. Controllers of this type often control synthesizers, but in principle they can also be assigned effect and filter parameters.
Infrared controllers, which correspond to optical control units and can be controlled by hand movements, also differ from other MIDI controllers. Due to their stepless nature, they are suitable for pitch shifter and filter or effect parameters.